Cross-scene GameObject and component references can be assigned into Init fields of client components that have an initializer.
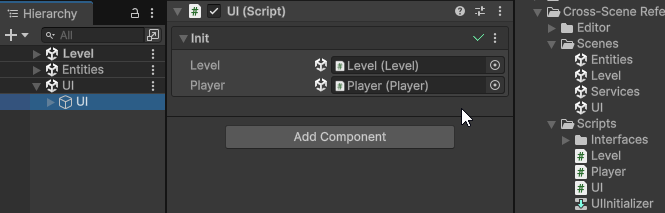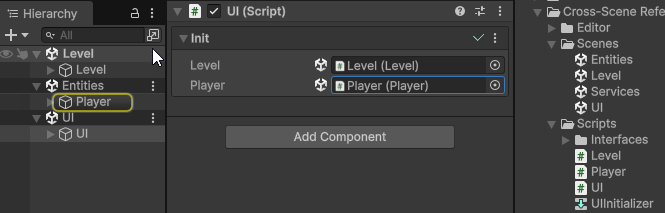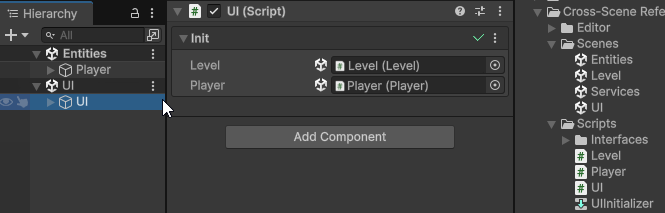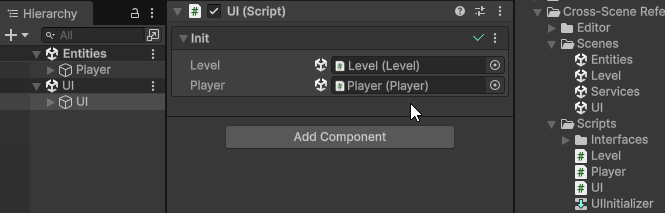
To assign a cross-scene reference, open multiple scenes in the Editor, and drag-and-drop a GameObject from a different scene into the Init field of the client component.
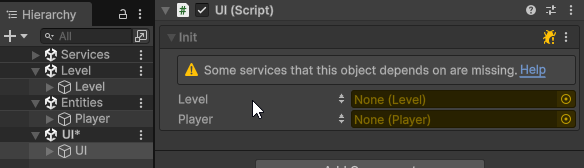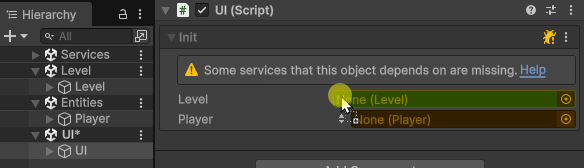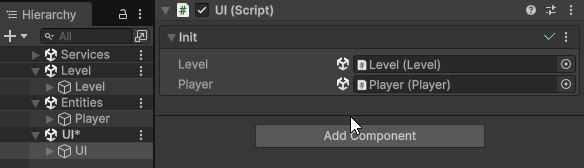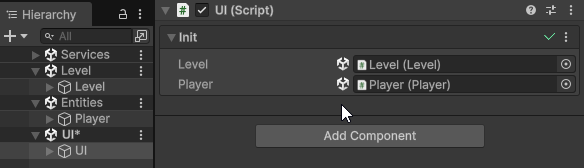
This will make Init(args) automatically generate a unique Cross-Scene Id for the assigned Object, and assign a value provider into the client’s Init field, which will be used to automatically resolve the cross-scene reference at runtime during initialization.
The cross-scene reference will persist even if the scene containing the dragged Object is unloaded in the Editor.
You can click the Object field to ping the referenced Object, if it’s currently loaded, or the scene asset that contains it, if it’s currently not loaded.
Asynchronous Initialization
At runtime, if you want the client to receive the Object from the other scene in its Init method immediately when the client’s scene finishes loading, you have to make sure to load the scene containing the referenced Object before the client’s scene.
If the client is loaded before the Object that it needs, the client will automatically be disabled and its initialization delayed, until the moment that the referenced Object becomes available (see MonoBehaviour<T>’s Asynchronous Initialization section for more details).
Any<TValue>
Any<TValue> type fields can also be used to support cross-scene references in addition to initializers.
Use Cases
- Scene Layers – splitting up level into multiple scene “layers” can help enabling multiple people to work on the same level in parallel without merge conflicts. E.g. static environment, dynamic entities, lighting, camera and logic could all be placed into separate scenes. Cross-scene references make it possible for components from these different scenes to reference each other when needed.
- World streaming – splitting a larger environment into multiple smaller scene chunks, and then loading and unload them dynamically as the player moves through the world, can help improve performance.
using Sisus.Init;
using UnityEngine;
public class Waypoint : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField] Any<Waypoint> previous; // <- these Waypoints could be
[SerializeField] Any<Waypoint> next; // in different scenes!
public Waypoint Previous => previous.Value;
public Waypoint Next => next.Value;
}
Best Practices
- When using cross-scene references, be mindful of the lifetimes of the two scenes; you should only use a cross-scene reference when both scenes are always loaded and unloaded together, or when the scene containing the referenced object remains loaded longer than the scene containing the client object.